Lecture Notes - CS441
Tuesday, September 10th 2024
-
On the speakers
- You have to be able to explain yourself and why you did the things you did for your project.
- What’s your experience as a student: your projects.
- Colleges generally use the same textbooks, therefore what makes your experience different? Why should I hire you?
- How you present yourself. How you solve the problem. Your experience. The foundations and classes you learned them from.
- Soft skills, don’t be a jerk.
- A recruiter thinks of three things when considering you:
- Are you an asset? Are you valuable or a liability?
- Are you a team player?
- Can you fit with the company culture?
- Team or by yourself? Both.
-
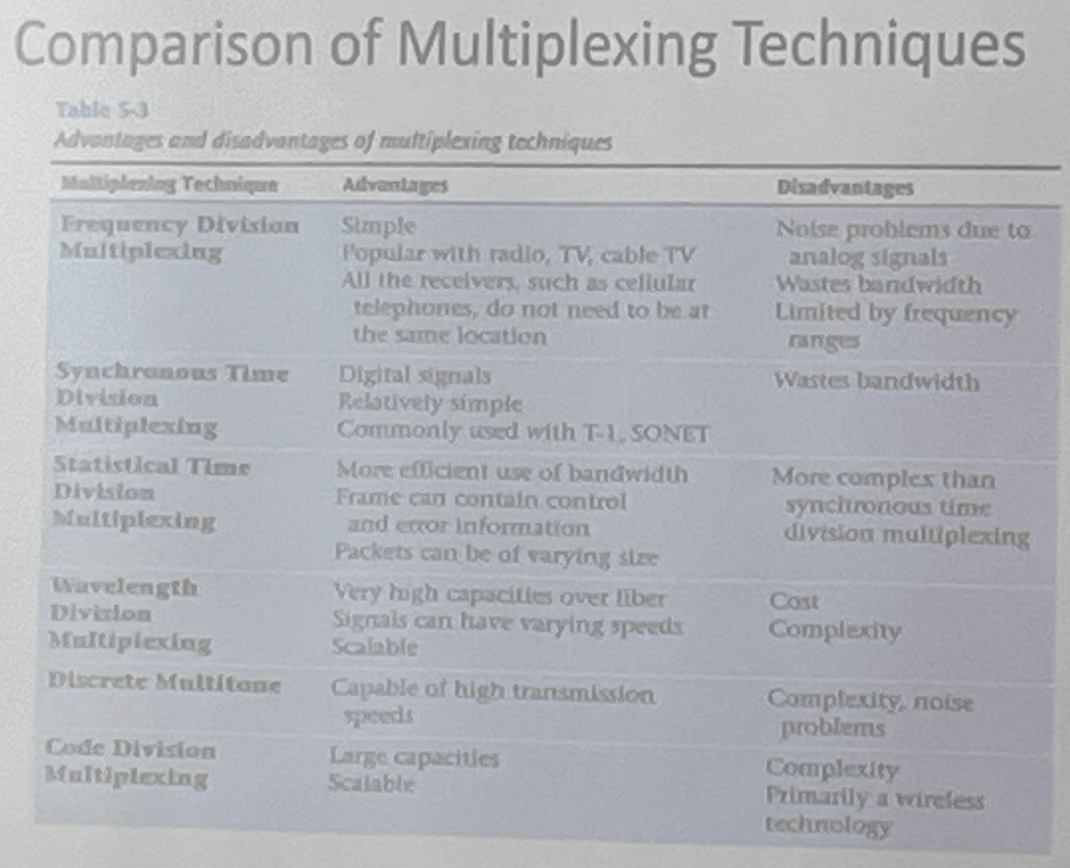
Multiplexing
- Why we have it
- Bandwidth is the most important part of computer networks
- It’s like highways
- Engineers have to optimize the highways
- Two ways to preserve the bandwidth
- Highway analogy: compression is like the 2+ or more lane on the highway
- Multiplexing is when you’re trying to get on the highway, the red/green light before you enter
- This is to ensure the highway runs smoothly, no traffic etc.
-
Introduction
- Under simplest conditions, medium can carry only one signal at any moment in time
- Medium: wire, wireless, Bluetooth, etc.
- Two types of multiplexing:
- Frequency division multiplexing
- Time division multiplexing
- (Also code division multiplexing)
-
Frequency Division Multiplexing
- Assignment of nonoverlapping frequency ranges to each “user” or signal on a medium
- For satellite sending channels 1-n to earth:
- Freq 0-10kHz
- Channel 1: 0-0.9kHz
- Channel 2: 1-1.9kHz
- Thus, all signals are transmitted at the same time
- Each channel is assigned a set of frequencies and is transmitted over the medium
- .
- AM - Amplitude modulation
- Change amplitude, depends on the power
- FM - Frequency modulation
- PM - Phase modulation
- Used by the army, uses the start of the sine wave, more difficult
- XM - Satellite modulation
-
FDM Continued
- Oldest multiplexing technique
-
Time Division Multiplexing
- Sharing of the signal is accomplished by dividing available transmission time on a medium among users
- Satellite:
- Channel 1: 1s
- Channel 2: 2s
- Channel 3: 3s
- Divided into two subdivision basic forms:
- Synchronous time division multiplexing
- Statistical time division multiplexing
- Digital signaling is used exclusively
-
Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing
- Original time division multiplexing
- Generated data faster than other devices
- Back to satellite, what if channel 2 is off the air? We waste the bandwidth in this case
- This is where you see test photos (the colors, circles, bars) to fill in the space
- Buffering as a result of too much info being sent from one channel, the circle becomes slower
-
Statistical Time Division Multiplexing
- This solved both above problems, it distributes the time, instead of 1s it’s 1.3s or 1.5s.
- A statistical multiplexor transmits the data from active workstations only.
- If workstation is not active, no space is wasted in the multiplexed system.
-
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
- Multiplexes multiple data streams into a single fiber-optic line
- Different wavelength lasers (called lambdas) transmit the multiple signals
-
Discrete Multitone
- A multiplexing technique commonly found in digital subscriber (DSL) systems
- DMT combines hundreds of different signals, or subchannels, into one stream
- Interestingly, all of these subchannels belong to a single user, unlike the previous multiplexing techniques
- In your house, you have a parking spot
- You don’t use it all the time, work, going out, etc.
- What if you came home and someone else was parked in your spot
- What the hell are you doing in my spot? It’s my spot.
- You have the right to kick the person out of the spot
- DSL the whole bandwidth connected to your house belongs to you
- This is why companies keep calling to combine internet, landline, phone to one line, because of this
-
Code Division Multiplexing
- What’s inside your cellphone
- Also known as code division multiple access
- An advanced technique that allows multiple devices to transmit on the same frequencies at the same time
- Each mobile device is assigned a unique 64-bit code
- We call cellphones cellphones because they are a part of a cell of transmission
- Fiber optics:
- First mile problem, when ISP send electrical signals, they have to convert to light for fiber optics
- Last mile problem, turning the light back into electrical signals
