Lecture Notes - CS441
Tuesday, August 27th 2024
- Previous slides are posted on Canvas
- Important: packet switching and circuit switching
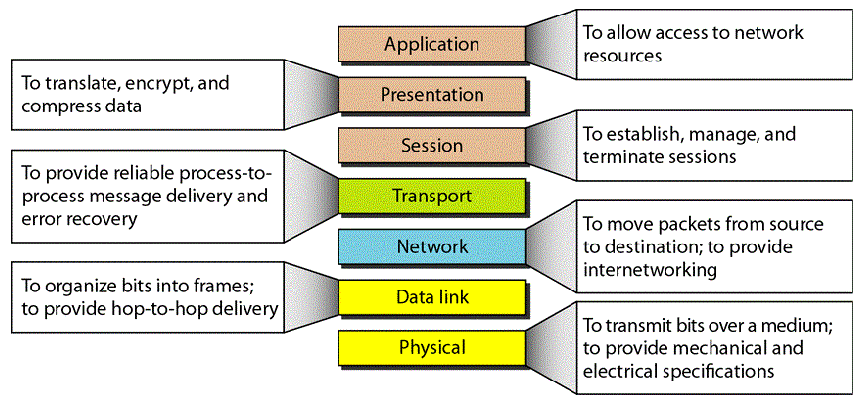
- Very important: OSI Model
- Application (Data)
- Presentation (Data)
- Session (Data)
- Transport (Segments)
- Network (Packets)
- Data Link (Frames)
- Physical (Bits)
- Above is a translation for what the OSI Model layers would do
- Transport: why we compress: bandwidth, our valued real estate
-
Understanding the big picture:
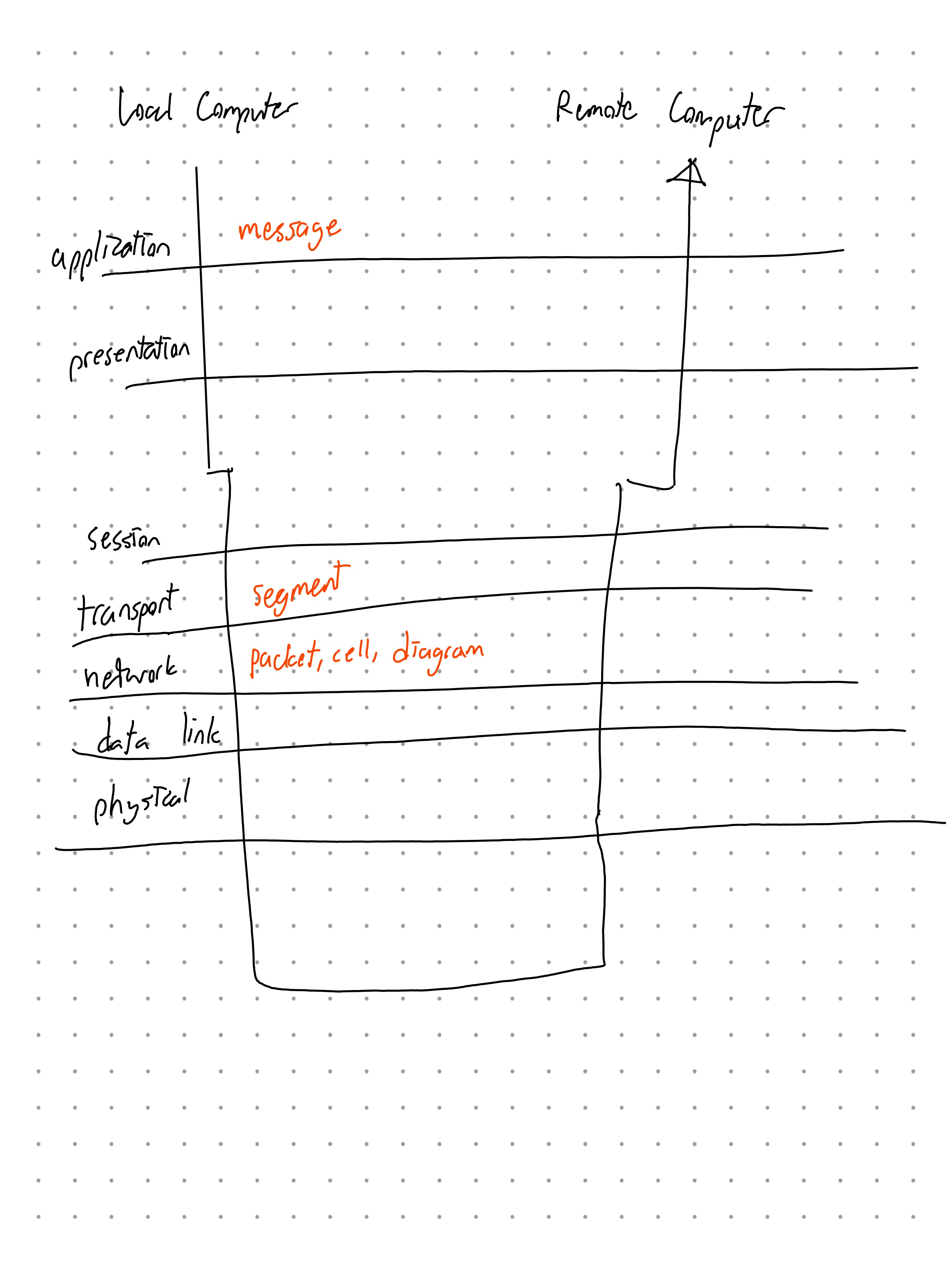
- End-to-end: before we send the data to the other party, we make sure the other party is there
- Same bandwidth
- Valid point of communication
- Transport: check if there is any error, cuts into segments
- Cuts into packets
- Physical: 0s and 1s are transported, then on the “other side”, the reverse happens:
- packets → segments → turns into message → shown to user
- We’ll cover standard packet size later
-
Application Layer
- HTTP
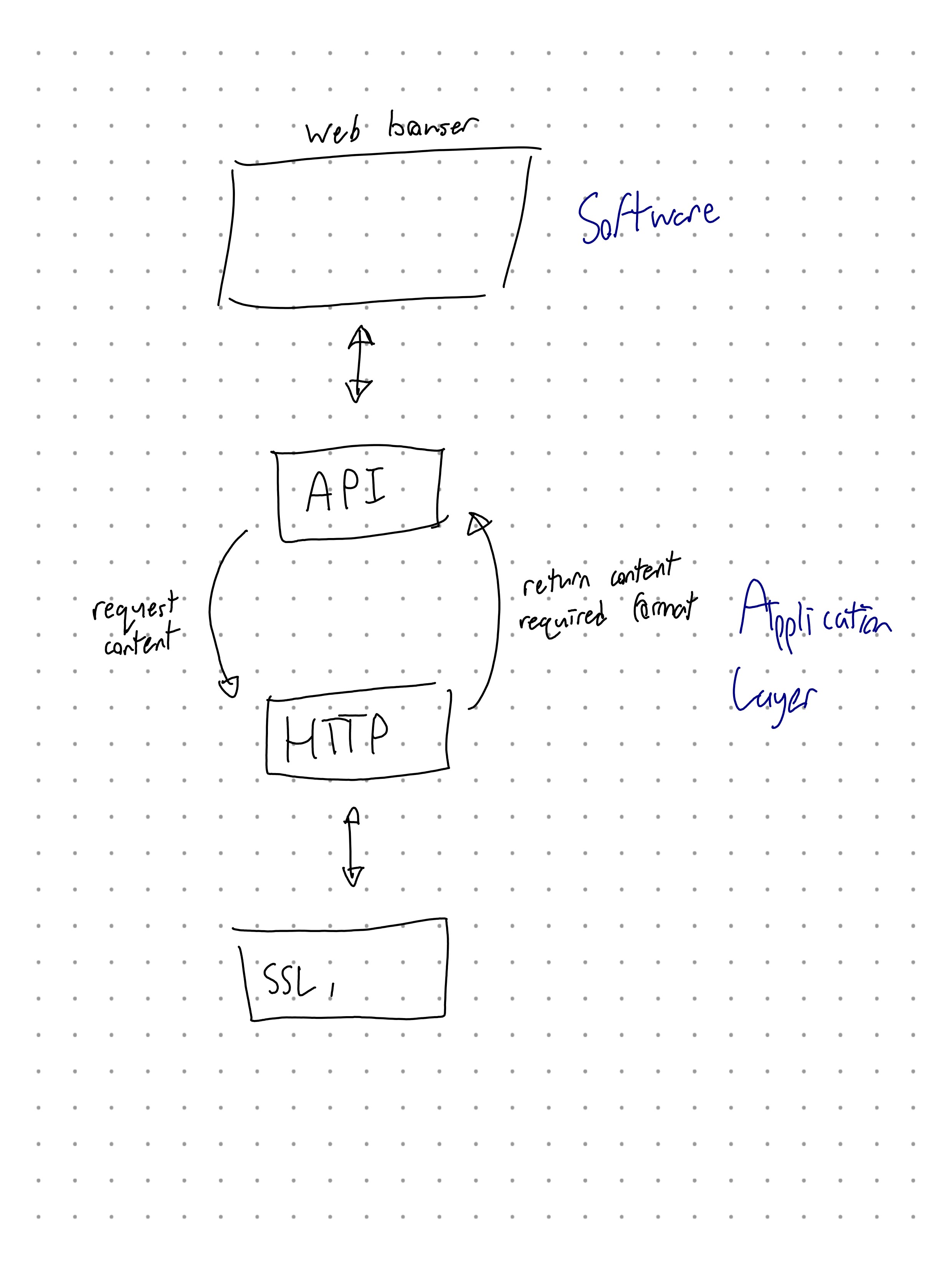
- DoorDash uses Google Maps API
- Example protocol: Security Session
-
Session Layer
- Least respected in the whole list
- Like a wedding: wedding holder is thankless hero in holding the wedding, everybody busy thanking the bride/groom
- Establishing and keeping alive communications link
- Keeping communications secure
- Identify session participants
- Synchronizing dialogue between two nodes
- Video chat, audio delay during talking
- “Still there”
- Possibility the connection will continue even if no communication is going on
-
Transport Layer
- TCP/IP
- Suite of protocols
- NEEDED if you want to connect to the internet
- Layer 4
- IP: Layer 3 (Network)
- MTU (Maximum transmission unit)
- Accepts data from Session Layer, they are trusting the Session Layer
- Manage end-to-end data delivery
- Like Amazon taking pictures of delivered package
- Acknowledgement of delivery
- Relying on “Still there → still there → still there”, aka async communication wouldn’t ever end
- Handle flow control
- Warehouse dumping/loading area; if warehouse is accepting 10 trucks a day and there’s suddenly 15, there’s traffic, aka overflow
- Stops intake unless processing is finished
- Quality of Service (QoS)
- Has a priority
- Ex. CFO, CEO has a zoom meeting, thus, bandwidth of an intern watching YouTube is lowered
- Examples of TCP
-
Network Layer
- Routers/Switches
- IP
- IPv4 - 232
- IPv6 - 2128
- What is the difference?
- IPv4 is 32bit, IPv6 is 128bit.
- What happened to IPv5?
- Was created to be a protocol for streaming services
- Don’t ever reuse the same term
- Example with Operating Systems
- Windows 7/8/10/11
- We didn’t have Windows 9 because of Windows 95/98
- Windows in the system is represented as 9x
-
Data Link Layered
- Two sublayers
- Logical Link Control (LLC)
- MAC (Media Access Control)
-
Physical Layer
- Copper transmission medium
- Signals issued as voltage
- Fiber-optic cable
- Signals issued as light pulses
- Wireless transmission medium
- Signals issued as electromagnetic signals


